-
Generally, cables can transmit information along their length. To actually get the information where it needs to go, you need to make the right connections to an RJ45 connector. Your cable run needs to terminate into a connector, which needs a jack to plug into. RJ45 is a standard type of physical connector for network cables, which is especially used for Ethernet networking. Recently, RJ45 connectors are commonly seen with Ethernet cables, and the Ethernet cables with RJ45 connectors are also called RJ45 cables. Today, we will explore the RJ45 connector.
RJ45 Connector
RJ45 connector is the most common twisted-pair connector for Ethernet cables and networks. “RJ” means “registered jack”, which is a standardized telecommunication network interface for connecting voice and data equipment to a service provided by a local exchange carrier or long distance carrier. The physical connectors that registered jacks use are mainly the modular connector and 50-pin miniature ribbon connector types. RJ45 connector is an 8-position, 8-contact (8P8C) modular plug and jack, which is commonly used to connect computers onto Ethernet-based local area networks (LAN). RJ45 cable plug is usually made of a plastic piece with eight pins on the port. Four of the pins are used for sending and receiving data, and the other four are used for other technologies or power networking devices.
Two Wiring Schemes of RJ45 Connector: T568A and T568B
As we all know, there are two wiring schemes: T568A and T568B, which are used to terminate the twisted-pair cable onto the connector interface. Two standards define how the RJ45 pinouts to arrange the individual eight wires when linking RJ45 connector to a cable. These wiring layouts have their own color convention, and following the convention is important to ensure electrical compatibility. The differences of T568A and T568B in color conventions are shown in the figure below.
With regard to the two standards, there are two different connectivity forms. The T-568B wiring scheme is by far the most common, though many devices support the T-568A wiring scheme as well. If both ends of the patch cords are wired on the basis of one standard, it is a straight through connection. Both the standards can be used for straight through cable. If not, it is a crossover connection. Some networking applications require a crossover Ethernet cable, which has a T-568A connector on one end and a T-568B connector on the other. This type of cable is typically used for direct computer-to-computer connections when there is no router, hub, or switch available.
RJ45 VS. RJ11
Several other types of connectors closely resemble RJ45, the RJ11 connector used with telephone cables is one of such connectors. The close physical similarity of RJ45 and RJ11 makes it difficult for an untrained eye to tell the two apart. RJ11 connector is a 6P2C (6 position 2 contact) modular connector - only uses six positions rather than eight positions, which make them less popular than RJ45 connectors.
RJ45 and RJ11 are two commonly used jacks, each with their own specific purpose. The biggest difference between them is that they are used for different applications. RJ45 is used in networking, where you connect computers or other network elements to each other. RJ11 is the cable connector that is being used in telephone sets. Aside from the application, another difference is the number of wires in their connectors. If you look closely at both connectors, you would see that there are only four wires inside an RJ11 while there are eight wires inside an RJ45. As a consequence, RJ45 connector is a little bit bigger than RJ11. It is then quite easy to deduce that you cannot plug in an RJ45 connector to a RJ11 slot but the opposite is possible. Although the smaller size of RJ11 makes it easier to be plugged into the RJ45 slot, it is not recommended to do so since this may damage the device that adopts the RJ45 slot. With proper knowledge and training, some people have been able to use RJ45s all over their house instead of RJ11s. At present, RJ45 jacks are usually placed on the wall outlets inside people’s houses to reduce the number of visible wiring when using VoIP handsets that are rapidly gaining popularity.
Main differences:
- RJ45 is used with Ethernet cables in computer networking while RJ11 is used in connecting telephone units.
- RJ45 contains more wires than RJ11.
- RJ45 is physically bigger than RJ11 to accommodate the extra wires.
Conclusion
RJ45 connectors are the key part of Ethernet connectivity to transmit voice and data media. They were developed as much smaller and cheaper replacements to the older telephone installation methods of hardwired cords. The easy plug-n-play style reduces the difficulty of installation. Compared with RJ11, RJ45 is suitable for more applications, such as Ethernet networking, telecommunications, factory automation and so on. And the RJ45 Ethernet cables are frequently used for networking devices, such as Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat7 etc.
 votre commentaire
votre commentaire
-
According to a recent survey, over half (57%) of companies have already adopted the Internet of Things (IoT) technology. By 2019, that statistic is projected to reach 85% as the expectations for IoT to deliver value and innovation continue to grow. Many advocates are struggling to secure IoT devices. To lead the pack in the switches markets, Cisco recently announced the Catalyst 9500 Series switches, which are designed for security, IoT and the cloud. The switches will be the next generation of the most widely deployed switching platform. Here in this article will take you to understand more about Catalyst 9500 switches and which optical transceivers are compatible for it.

Cisco Catalyst 9500 Switches - Built for Security, IoT, and Cloud
The Cisco catalyst 9500 series switches are the next generation of enterprise-class core and aggregation layer switches, which are part of the new Cisco catalyst 9000 family. These switches come with 4-core 2.4-GHz CPU, 16-GB DDR4 memory and 16-GB internal storage. The catalyst 9500 comes in three different varieties: Catalyst 9500-24Q, Catalyst 9500-12Q and Catalyst 9500-40X. They support 10G and 40G Gigabit Ethernet network connection. The most important feature is that these switches support the advanced routing and infrastructure services, such as MPLS L2/L3 VPNs and MVPN. And they are designed for full fabric-control with Cisco DNA and Software-Defined Access (SD-Access). Therefore, these switches deliver stellar performance and functionality and extend Cisco’s networking leadership with significant innovations in security, mobility, IoT and cloud.
Model Description Total QSFP or SFP+ Ports Catalyst 9500-24Q Cisco catalyst 9500 series 24-port 40 Gigabit Ethernet with QSFP 24 QSFP/24 SFP+ Catalyst 9500-12Q Cisco catalyst 9500 series 12-port 40 Gigabit Ethernet with QSFP 12 QSFP/12 SFP+ Catalyst 9500-40X Cisco catalyst 9500 series 40-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet with SFP+ 40 SFP+ Software-Defined Access for Cisco Catalyst 9500 Switches
The Cisco catalyst 9500 series switches form the foundational building block for Software-Defined Access. Software-Defined Access is the industry’s first intent-based networking solution for the Enterprise built on the principles of Cisco’s Digital Network Architecture (DNA). It is an open and extensible, software-driven architecture that accelerates and simplifies your enterprise network operations. The programmable architecture frees your IT staff from time-consuming, repetitive network configuration tasks. Compared catalyst 9500 to the older switches, it performs more benefits for customers:
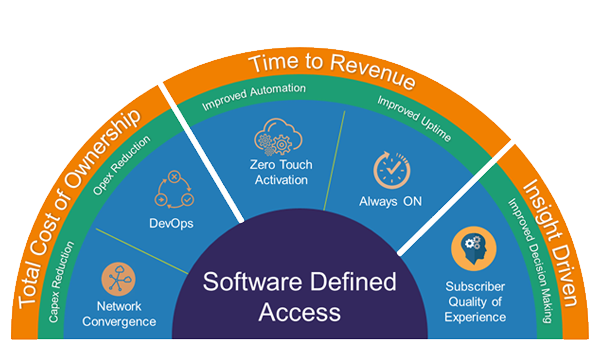
- Reduced cost and complexity with Cisco Software-Defined Access by automating policy, enabling fast service creation and providing complete visibility into the wired and wireless access networks.
- Create better customer and employee experiences through higher performance and improved support for mobility and new apps.
- Advanced end-to-end security to handle threats before, during and after attacks.
Compatible QSFP+ / SFP+ Transceivers for Cisco Catalyst 9500 Switches
According to Cisco 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver Modules Compatibility Matrix, C9500-12Q, C9500-24Q and C9500-40X can support SFP-10G-ER, SFP-10G-ZR, SFP-10G-ER-S, SFP-10G-ZR-S, QSFP-40G-SR4, QSFP-40G-LR4, SFP-40G-SR4-S ect. All SFP+ and QSFP+ transceivers can be found in FS.COM. And all of these cost-effective compatible modules have been strictly tested to make sure 100% compatibility.
QSFP+ Transceivers
Transceiver Model Part ID Transceiver Description QSFP-40G-SR4 36157 Cisco QSFP-40G-SR4 Compatible 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ 850nm 150m MTP/MPO DOM Transceiver, $ 49.00 QSFP-40G-CSR4 36165 Cisco QSFP-40G-CSR4 Compatible 40GBASE-CSR4 QSFP+ 850nm 400m MTP/MPO DOM Transceiver, $ 59.00 QSFP-40G-SR4-S 36143 Cisco QSFP-40G-SR4-S Compatible 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ 850nm 150m MTP/MPO DOM Transceiver, $ 49.00 QSFP-40G-LR4 36170 Cisco QSFP-40G-LR4 Compatible 40GBASE-LR4 and OTU3 QSFP+ 1310nm 10km LC DOM Transceiver, $ 340.00 QSFP-40G-LR4-S 36153 Cisco QSFP-40G-LR4-S Compatible 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ 1310nm 10km LC DOM Transceiver, $ 340.00 QSFP-40G-ER4 36173 Cisco QSFP-40G-ER4 Compatible 40GBASE-ER4 and OTU3 QSFP+ 1310nm 40km LC DOM Transceiver, $ 1,500.00 QSFP-40G-SR-BD 48722 Cisco QSFP-40G-SR-BD Compatible 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional Duplex LC Transceiver, $ 300.00 WSP-Q40GLR4L (except C9500-40X ) 36172 Cisco WSP-Q40GLR4L Compatible 40GBASE-LR4L QSFP+ 1310nm 2km LC DOM Transceiver, $ 340.00 SFP+ Transceivers
Transceiver Model Part ID Transceiver Description SFP-10G-SR 11552 Cisco SFP-10G-SR Compatible 10GBASE-SR SFP+ 850nm 300m DOM Transceiver, $ 16.00 SFP-10G-SR-S 36433 Cisco SFP-10G-SR-S Compatible 10GBASE-SR SFP+ 850nm 300m DOM Transceiver, $ 16.00 SFP-10G-LR 11555 Cisco SFP-10G-LR Compatible 10GBASE-LR SFP+ 1310nm 10km DOM Transceiver,$ 34.00 SFP-10G-LR-S 36434 Cisco SFP-10G-LR-S Compatible 10GBASE-LR SFP+ 1310nm 10km DOM Transceive, $ 34.00 SFP-10G-LRM (except C9500-24Q / C9500-12Q ) 11556 Cisco SFP-10G-LRM Compatible 10GBASE-LRM SFP+ 1310nm 220m DOM Transceiver, $ 34.00 SFP-10G-ER 11557 Cisco SFP-10G-ER Compatible 10GBASE-ER SFP+ 1550nm 40km DOM Transceiver, $ 149.00 SFP-10G-ER-S 36435 Cisco SFP-10G-ER-S Compatible 10GBASE-ER SFP+ 1550nm 40km DOM Transceiver, $ 149.00 SFP-10G-ZR 11582 Cisco SFP-10G-ZR Compatible 10GBASE-ZR/ZW and OTU2e SFP+ 1550nm 80km DOM Transceiver,$ 299.00 SFP-10G-ZR-S 36436 Cisco SFP-10G-ZR-S Compatible 10GBASE-ZR/ZW and OTU2e SFP+ 1550nm 80km DOM Transceiver,$ 299.00 Note: for C9500-24Q / C9500-12Q, the Transceivers should be used with CVR-QSFP-SFP10G.
Conclusion
The catalyst 9500 switches solve some persistent challenges of enterprise networks by utilizing platform innovations built around four key areas: security, Internet of Things (IoT) convergence, mobility and cloud readiness. There is no doubt that catalyst 9500 is leading us to a new era of faster and securer network.
 votre commentaire
votre commentaire Suivre le flux RSS des articles
Suivre le flux RSS des articles Suivre le flux RSS des commentaires
Suivre le flux RSS des commentaires



